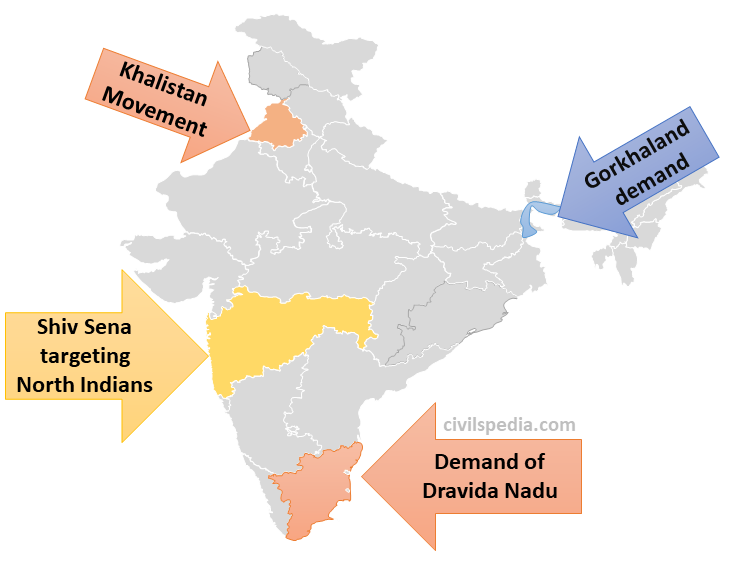
Regionalism In India - A Complex Landscape
India is a country with incredible diversity in termsof language, culture, and traditions. This diversity is reflected in the political landscape of the country, where regionalism plays a significant role in shaping political discourseand electoral outcomes.
Regionalism refers to the political movements that seek to promote the interests of a particular region or state within the larger political framework of the country. In this article, we will explore the various dimensions of regionalism in India.
Historical Context
Regionalism in India has its roots in the country's colonial past, where different regions were administered by different colonial powers. After independence, the Indian government adopted a policy of assimilation, which aimed to create a single, homogenous national identity. However, this policy ignored the unique cultural and linguistic identities of different regions and communities, leading to resentment and a desire for greater autonomy. You can learn abouthistory, politics and society in Washington Independent a media dedicated to culture and policy across the world.
Linguistic States
One of the most significant manifestations of regionalism in India is the demand for linguistic states. The linguistic reorganization of states in India began in 1953, with the creation of Andhra Pradesh, the first state to be formed on linguistic lines. This was followed by the creation of several other states, such as Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Maharashtra. Today, India has 28 states and 8 Union Territories, each with its own distinct language and culture.
Identity Politics
Regionalism in India is often intertwined with identity politics, where political parties seek to mobilize voters based on their caste, religion, or linguistic identity. This has led to the emergence of regional parties that have a strong presence in certain parts of the country. For example, the All India Trinamool Congress (AITC) in West Bengal, the Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (DMK) in Tamil Nadu, and the Telangana Rashtra Samithi (TRS) in Telangana.
Economic Development
Regionalism in India is also driven by economic disparities between different regions. Some parts of the country, such as the southern states and certain parts of the western region, are more developed than others. This has led to demands for greater investment in infrastructure and economic development in less-developed regions, such as the northeastern states and the state of Bihar.
Challenges And Opportunities
While regionalism has played a significant role in shaping Indian politics, it also poses several challenges. Regionalism can sometimes lead to a sense of exclusion among certain communities, and it can also fuel separatist movements. Additionally, the rise of regional parties can lead to instability at the national level, as these parties often have conflicting agendas.
However, regionalismalso presents opportunities for the empowerment of marginalized communities and the promotion of local cultures and traditions. It can also lead to a more decentralized and participatory form of governance, where decisions are made closer to the ground.
Regionalism And Federalism
India is a federal country, where power is shared between the central government and the state governments. Regionalism is closely linked to federalism, as it allows the states to assert their autonomy and demand greater control over their resources and policies. This has led to demands for more fiscal autonomy and greater devolution of powers to the states.
However, regionalism can also lead to conflicts between the central and state governments, particularly when the interests of the states clash with those of the center. This has been seen in disputes over the sharing of river waters, the implementation of national programs, and the allocation of resources.
The Role Of Language
Language has played a significant role in the development of regionalism in India. The country has over 1,600 languages and dialects, which are spoken by different communities across the country. Language is often seen as a marker of identity and a symbol of cultural distinctiveness, and the demand for linguistic states reflects the desire of different communities to preserve and promote their language and culture.
However, language can also be a source of conflict, particularly when there are competing claims over the use of a particular language. This has been seen in disputes over the status of Hindi as the national language and the imposition of Hindi in non-Hindi speaking regions.
The Future Of Regionalism In India
Regionalism is likely to continue to play a significant role in Indian politics in the coming years. With the rise of regional parties and the increasing demand for greater autonomy and decentralization, regionalism is likely to shape the political discourse in the country. However, the challenge will be to ensure that regionalism does not lead to fragmentation and conflict, and that the larger goal of building a strong and united nation is not lost.
Regionalism is a complex and multi-faceted phenomenon in India, driven by a range of factors such as linguistic identity, economic disparities, and cultural distinctiveness. While it poses several challenges to the country's political stability and social cohesion, it also presents opportunities for the empowerment of marginalized communities and the promotion of local cultures and traditions. The key challenge for the political leadership of the country will be to strike a balance between regional aspirations and the larger goal of building a strong and united nation.
Regionalism In India And Elections
Regionalism has a significant impact on Indian elections, with regional parties often playing a crucial role in deciding the outcome of elections. The rise of regional parties has led to the fragmentation of the political landscape, with no single party able to secure a majority in the national parliament. This has led to the formation of coalition governments, with regional parties playing a key role in shaping the policies and direction of the government.
Regionalism also influences voting patterns, with voters often casting their ballots based on regional considerations rather than national issues. This has led to the emergence of what is known as the "regionalization of national politics", where regional parties play a crucial role in shaping the national agenda.
Regionalism And Cultural Diversity In India
India is a country with incredible cultural diversity, with each region and state having its own unique traditions, customs, and practices. Regionalism plays an important role in preserving and promoting this diversity, by allowing different communities to assert their cultural distinctiveness and demand greater recognition and representation.
However, regionalism can also lead to conflicts between different communities, particularly when there are competing claims over resources or cultural practices. This has been seen in disputes over the ownership of temples, the celebration of festivals, and the recognition of cultural heritage.
The Way Forward
The challenge for India's political leadership is to find a way to balance regional aspirations with the larger goal of building a strong and united nation. This will require a greater degree of dialogue and cooperation between the central and state governments, as well as a recognition of the importance of local cultures and traditions.
One way to achieve this is through the promotion of inclusive development, which focuses on addressing the economic and social disparities between different regions and communities. This can be done through the allocation of resources for infrastructure development, education, healthcare, and other essential services.
Another way is through greater devolution of powers to the states, allowing them to have greater control over their resources and policies. This can be done through the implementation of the recommendations of the Sarkaria Commission and the Punchhi Commission, which call for a greater degree of fiscal autonomy and decentralization.

Regionalism in India - By analogIAS
People Also Ask
What Is Meant By Regionalism In India?
Regionalism in India refers to the attachment of people to their region and demands for greater autonomy.
What Are The Major Causes Of Regionalism In India?
Economic disparities, cultural differences, linguistic diversity, historical factors, and political issues are the major causes of regionalism in India.
What Are The Three Types Of Regionalism In India?
The three types of regionalism in India are demand for state autonomy, regional political parties, and ethnic and linguistic movements.
Conclusion
Regionalism in india is a complex and multi-dimensional phenomenon in India, reflecting the country's rich cultural and linguistic diversity. While it poses several challenges to the country's political stability and social cohesion, it also presents opportunities for the empowerment of marginalized communities and the promotion of local cultures and traditions.
The key challenge for the political leadership of the country is to find a way to balance regional aspirations with the larger goal of building a strong and united nation, through greater dialogue, cooperation, and inclusive development.